Transformation algorithms.
Modules | |
| lazy | |
Typedefs | |
| template<typename List , typename State , typename Fun > | |
| using | meta::accumulate = fold< List, State, Fun > |
An alias for meta::fold. More... | |
| template<typename ListOfLists > | |
| using | meta::cartesian_product = reverse_fold< ListOfLists, list< list<> >, quote_trait< detail::cartesian_product_fn > > |
Given a list of lists ListOfLists, return a new list of lists that is the Cartesian Product. Like the sequence function from the Haskell Prelude. More... | |
| template<typename... Lists> | |
| using | meta::concat = _t< detail::concat_< Lists... > > |
| Concatenates several lists into a single list. More... | |
| template<typename List , typename N > | |
| using | meta::drop = _t< detail::drop_< List, N > > |
Return a new meta::list by removing the first N elements from List. More... | |
| template<typename List , std::size_t N> | |
| using | meta::drop_c = _t< detail::drop_< List, meta::size_t< N > >> |
Return a new meta::list by removing the first N elements from List. More... | |
| template<typename List , typename Pred > | |
| using | meta::filter = join< transform< List, detail::filter_< Pred > >> |
Returns a new meta::list where only those elements of List that satisfy the Callable Pred such that invoke<Pred,A>::value is true are present. That is, those elements that don't satisfy the Pred are "removed". More... | |
| template<typename List , typename State , typename Fun > | |
| using | meta::fold = _t< detail::fold_< List, id< State >, Fun > > |
Return a new meta::list constructed by doing a left fold of the list List using binary Callable Fun and initial state State. That is, the State_N for the list element A_N is computed by Fun(State_N-1, A_N) -> State_N. More... | |
| template<typename ListOfLists > | |
| using | meta::join = apply< quote< concat >, ListOfLists > |
| Joins a list of lists into a single list. More... | |
| template<typename List , typename Pred > | |
| using | meta::partition = fold< List, pair< list<>, list<> >, detail::partition_< Pred > > |
Returns a pair of lists, where the elements of List that satisfy the Callable Pred such that invoke<Pred,A>::value is true are present in the first list and the rest are in the second. More... | |
| template<typename List > | |
| using | meta::pop_front = _t< detail::pop_front_< List > > |
Return a new meta::list by removing the first element from the front of List. More... | |
| template<typename List , typename T > | |
| using | meta::push_back = _t< detail::push_back_< List, T > > |
Return a new meta::list by adding the element T to the back of List. More... | |
| template<typename List , typename T > | |
| using | meta::push_front = _t< detail::push_front_< List, T > > |
Return a new meta::list by adding the element T to the front of List. More... | |
| template<typename List , typename T , typename U > | |
| using | meta::replace = _t< detail::replace_< List, T, U > > |
Return a new meta::list where all instances of type T have been replaced with U. More... | |
| template<typename List , typename C , typename U > | |
| using | meta::replace_if = _t< detail::replace_if_< List, C, U > > |
Return a new meta::list where all elements A of the list List for which invoke<C,A>::value is true have been replaced with U. More... | |
| template<typename List > | |
| using | meta::reverse = _t< detail::reverse_< List > > |
Return a new meta::list by reversing the elements in the list List. More... | |
| template<typename List , typename State , typename Fun > | |
| using | meta::reverse_fold = _t< detail::reverse_fold_< List, State, Fun > > |
Return a new meta::list constructed by doing a right fold of the list List using binary Callable Fun and initial state State. That is, the State_N for the list element A_N is computed by Fun(A_N, State_N+1) -> State_N. More... | |
| template<typename List , typename Pred > | |
| using | meta::sort = _t< detail::sort_< List, Pred > > |
Return a new meta::list that is sorted according to Callable predicate Pred. More... | |
| template<typename... Args> | |
| using | meta::transform = _t< detail::transform_< list< Args... > >> |
Return a new meta::list constructed by transforming all the elements in List with the unary Callable Fun. transform can also be called with two lists of the same length and a binary Callable, in which case it returns a new list constructed with the results of calling Fun with each element in the lists, pairwise. More... | |
| template<typename ListOfLists > | |
| using | meta::transpose = fold< ListOfLists, repeat_n< size< front< ListOfLists > >, list<> >, bind_back< quote< transform >, quote< push_back > >> |
Given a list of lists of types ListOfLists, transpose the elements from the lists. More... | |
| template<typename List > | |
| using | meta::unique = fold< List, list<>, quote_trait< detail::insert_back_ > > |
Return a new meta::list where all duplicate elements have been removed. More... | |
| template<typename ListOfLists > | |
| using | meta::zip = transpose< ListOfLists > |
Given a list of lists of types ListOfLists, construct a new list by grouping the elements from the lists pairwise into meta::lists. More... | |
| template<typename Fun , typename ListOfLists > | |
| using | meta::zip_with = transform< transpose< ListOfLists >, uncurry< Fun > > |
Given a list of lists of types ListOfLists and a Callable Fun, construct a new list by calling Fun with the elements from the lists pairwise. More... | |
| using meta::accumulate = typedef fold<List, State, Fun> |
| using meta::cartesian_product = typedef reverse_fold<ListOfLists, list<list<> >, quote_trait<detail::cartesian_product_fn> > |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Given a list of lists ListOfLists, return a new list of lists that is the Cartesian Product. Like the sequence function from the Haskell Prelude.
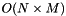 , where
, where 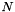 is the size of the outer list, and
is the size of the outer list, and 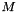 is the size of the inner lists.
is the size of the inner lists.
|
related |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Concatenates several lists into a single list.
meta::list. 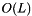 where
where 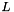 is the number of lists in the list of lists.
is the number of lists in the list of lists.
|
related |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list by removing the first N elements from List.
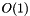 .
. | using meta::drop_c = typedef _t<detail::drop_<List, meta::size_t<N> >> |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list by removing the first N elements from List.
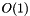 .
.
|
related |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Returns a new meta::list where only those elements of List that satisfy the Callable Pred such that invoke<Pred,A>::value is true are present. That is, those elements that don't satisfy the Pred are "removed".
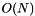 .
. | using meta::fold = typedef _t<detail::fold_<List, id<State>, Fun> > |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list constructed by doing a left fold of the list List using binary Callable Fun and initial state State. That is, the State_N for the list element A_N is computed by Fun(State_N-1, A_N) -> State_N.
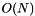 .
.
|
related |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Joins a list of lists into a single list.
meta::list<T...> where each T is itself an instantiation of meta::list. 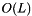 where
where 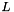 is the number of lists in the list of lists.
is the number of lists in the list of lists. | using meta::partition = typedef fold<List, pair<list<>, list<> >, detail::partition_<Pred> > |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Returns a pair of lists, where the elements of List that satisfy the Callable Pred such that invoke<Pred,A>::value is true are present in the first list and the rest are in the second.
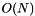 .
. | using meta::pop_front = typedef _t<detail::pop_front_<List> > |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list by removing the first element from the front of List.
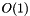 .
. | using meta::push_back = typedef _t<detail::push_back_<List, T> > |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list by adding the element T to the back of List.
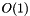 .
. pop_back not provided because it cannot be made to meet the complexity guarantees one would expect. | using meta::push_front = typedef _t<detail::push_front_<List, T> > |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list by adding the element T to the front of List.
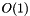 .
.
|
related |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list where all instances of type T have been replaced with U.
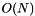 .
.
|
related |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list where all elements A of the list List for which invoke<C,A>::value is true have been replaced with U.
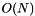 .
.
|
related |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list by reversing the elements in the list List.
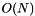 .
. | using meta::reverse_fold = typedef _t<detail::reverse_fold_<List, State, Fun> > |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list constructed by doing a right fold of the list List using binary Callable Fun and initial state State. That is, the State_N for the list element A_N is computed by Fun(A_N, State_N+1) -> State_N.
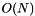 .
.
|
related |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list that is sorted according to Callable predicate Pred.
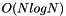 Worst case:
Worst case: 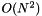 .
.
|
related |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list constructed by transforming all the elements in List with the unary Callable Fun. transform can also be called with two lists of the same length and a binary Callable, in which case it returns a new list constructed with the results of calling Fun with each element in the lists, pairwise.
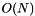 .
. | using meta::transpose = typedef fold<ListOfLists, repeat_n<size<front<ListOfLists> >, list<> >, bind_back<quote<transform>, quote<push_back> >> |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Given a list of lists of types ListOfLists, transpose the elements from the lists.
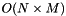 , where
, where 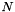 is the size of the outer list, and
is the size of the outer list, and 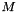 is the size of the inner lists.
is the size of the inner lists.
|
related |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Return a new meta::list where all duplicate elements have been removed.
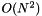 .
. #include <meta/meta.hpp>
Given a list of lists of types ListOfLists, construct a new list by grouping the elements from the lists pairwise into meta::lists.
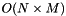 , where
, where 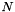 is the size of the outer list, and
is the size of the outer list, and 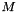 is the size of the inner lists.
is the size of the inner lists.
|
related |
#include <meta/meta.hpp>
Given a list of lists of types ListOfLists and a Callable Fun, construct a new list by calling Fun with the elements from the lists pairwise.
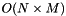 , where
, where 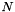 is the size of the outer list, and
is the size of the outer list, and 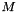 is the size of the inner lists.
is the size of the inner lists.